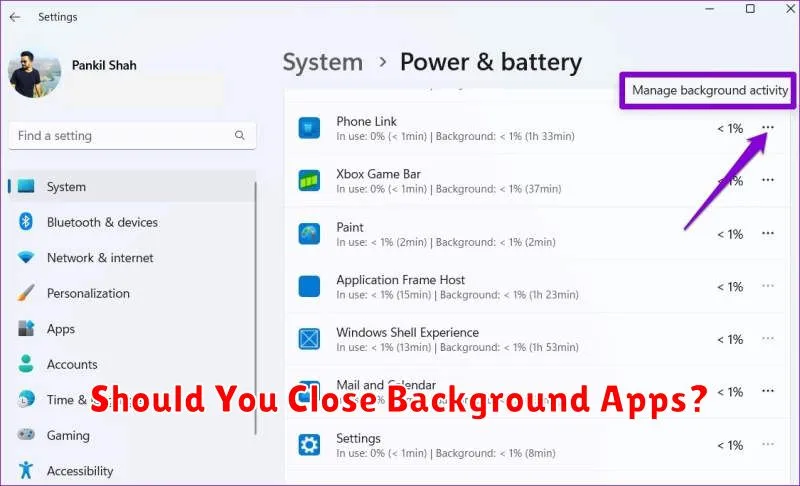
Do you frequently find yourself closing background apps on your phone or computer, hoping to boost performance or save battery life? Many users wonder if these actions are truly necessary, or if they’re simply a digital habit. This article will delve into the complexities of background apps, exploring their impact on system resources like CPU usage, memory, and battery drain. We’ll examine the differences between operating systems, like Android and iOS, and their respective approaches to background app management.
Understanding how background apps function is crucial for making informed decisions about whether to close them. We’ll discuss the benefits and drawbacks of allowing apps to run in the background, considering factors such as app refresh rates and the impact on overall system performance. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped to decide if closing background apps is genuinely beneficial, or if it’s an unnecessary practice for your particular device and usage patterns. Let’s explore the world of background app management and empower you to make the best choices for your device’s performance and battery life.
What Are Background Apps?
Background apps are applications that continue to run on your device even when you’re not actively using them. They aren’t visible on your screen like active apps, but they still consume system resources like processing power, battery life, and data. They often perform tasks such as syncing data, receiving notifications, or updating content.
Think of it like this: when you minimize an app instead of fully closing it, it moves to the background. It’s still operational, but it’s not taking center stage on your device’s screen.
There are two main types of background apps: those that are actively running processes and those that are in a suspended state. Actively running background apps are constantly working, while suspended apps are essentially frozen, consuming minimal resources until needed again.
Impact on Battery Life
One of the most common reasons users close background apps is the perceived impact on battery life. While it’s true that running apps consume power, the effect of background apps on modern mobile operating systems is often overstated.
Actively running apps, particularly those using GPS, camera, or intense processing, do consume significant battery. However, operating systems like iOS and Android employ sophisticated power management techniques that drastically limit the resources available to background apps.
Inactive background apps are generally in a suspended state, using minimal battery. The system suspends these apps, freeing up processor, memory, and network resources. While they technically remain “open”, their impact is negligible.
Closing background apps constantly can actually have a negative impact on battery. Relaunching apps requires more power than resuming a suspended app. The system has to load the app from storage, initialize its components, and allocate resources, all of which consumes battery.
Android vs iOS Behavior

Understanding how Android and iOS handle background apps is crucial to answering whether you should close them. The two operating systems employ fundamentally different approaches.
Android adopts a more liberal approach, allowing apps to run in the background more freely. This facilitates multitasking and quick resumption of previously used apps. However, excessive background activity can consume more battery power and system resources. Android employs a system of prioritizing apps, automatically closing less important ones when resources are scarce.
iOS takes a stricter approach to background app management. Background apps are typically quickly “frozen” and suspended. This conserves battery life and maintains system performance. While background refresh functionality exists for certain apps, iOS limits background activity significantly more than Android. This means apps are generally less demanding on resources when not actively in use.
When Closing Apps Helps
While modern operating systems are generally proficient at managing background apps, there are specific instances where manually closing them can prove beneficial.
Troubleshooting Performance Issues
If your device is experiencing slowdowns, unresponsiveness, or overheating, a rogue app running in the background might be the culprit. Closing unnecessary apps can free up processing power and memory, potentially resolving the issue. This is especially true for older devices with limited resources.
Extending Battery Life
Although background apps often consume minimal power, some, particularly those using location services or constantly syncing data, can significantly drain your battery. Closing these power-hungry apps can help extend your device’s battery life, especially crucial when you’re away from a charger.
Resolving App Malfunctions
Occasionally, apps may encounter glitches or become unresponsive. Closing and restarting the affected app can often resolve these software conflicts, restoring proper functionality.
Battery Saver Settings to Use
Modern operating systems offer built-in battery saver settings that can significantly extend the battery life of your devices. These settings typically work by limiting background activity, reducing screen brightness, and optimizing performance. Utilizing these features can be more effective than manually closing apps.
Low Power Mode/Battery Saver: This is a common setting found on most devices. Enabling this feature often restricts background app activity, reduces screen brightness, and limits data usage.
Background App Restrictions: Some operating systems allow you to specifically control which apps can run in the background. Restricting background activity for power-hungry apps can save significant battery power.
Adaptive Battery/Optimized Battery Usage: These features use machine learning to understand your usage patterns and optimize battery consumption accordingly. They prioritize battery usage for apps you use most frequently.
Location Services: Limiting the use of location services, especially to “while using the app,” can improve battery life. Constant GPS usage can drain your battery quickly.
Myths vs Facts
There are several misconceptions surrounding the practice of closing background apps. Let’s clarify the reality behind these common myths.
Myth 1: Closing background apps saves battery life significantly.
Fact: While apps running active tasks in the background consume battery, simply residing in the background has minimal impact. The operating system freezes inactive apps, preventing significant battery drain. Closing them constantly can actually use more battery due to the process of relaunching.
Myth 2: Closing background apps improves performance.
Fact: Modern operating systems efficiently manage memory and processing power. Unless an app is malfunctioning or actively using resources, it won’t noticeably affect performance. Closing apps unnecessarily can actually hinder performance as the system needs to reload them from scratch when needed.
Myth 3: Background apps constantly consume mobile data.
Fact: Background apps are generally restricted from using mobile data unless you’ve specifically granted permission. They might periodically check for updates or notifications, but this data usage is typically negligible.
Best Practices for Everyday Use
Managing background apps effectively can improve device performance and battery life. While completely closing all apps isn’t always necessary, understanding how to control them is crucial. Prioritize closing apps that consume significant resources, such as games or video streaming platforms, when not in use.
For frequently used apps, leaving them open can actually be more efficient than constantly reopening them. The operating system manages these background processes intelligently. However, periodically clearing apps from the background can prevent potential issues and free up resources.
Be mindful of apps that continuously run location services or background data refresh. Limiting these functionalities to only the essential apps can significantly improve battery life. Utilize your device’s built-in settings to monitor and control background app activity.